Which personal style should managers adopt to ensure success? What is the most effective approach to managing the work of subordinates? These questions have been extensively researched and debated over the last century, and while the general consensus has moved away from ‘command and control’ to management and leadership towards more consultative and participative approaches, there is no single ideal, as the best approach may vary according to circumstances and individual characteristics” (CMI 2013).
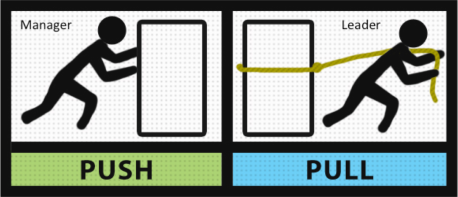
Management and leadership are different but both have similaries. Basically, managers perform functions in organisations. Managers hold titles and power to manage organisations. For example, a marketing brand manager is responsible for the marketing of products. They are also responsible for the performance and productivity of their subordinates. Fayol’s theory (1949) describes management is often have to do with planning, organisation, directing and controlling the activities of staff. However, leaders aim to influence and guide others to achieve particular objectives of the future. They have the ability to inspire and stimulate others to look upon and follow them. Leadership shows the power of an individual and often focused on changing attitudes.
Zaleznik (1977) suggests that managers adopt a less emotional and more passive attitude than leaders and are more concerned with seeking compromise in conflicting positions and with conserving order than in initiating transformation.
However, although management and leadership have different functions in organisations, they have somehow show similarities with each other. Leadership qualities may have revealed from a manager on particular occasions. Certainly, Mintzberg (1973) has mentioned leaders’ roles as one of his ten roles of management. Others, such as Handy (1993), Watson (1983) and Kotter (1990), suggest that leadership is simply part of broader role of management: a leader, focused attitudinal and organisation change, employing all the political, emotional and symbolic tools of leadership, might also conduct normal managerial responsibilities.
Based on my research, I believe transformation leadership is the most effective approach to managing the work of subordinates. Transformational leaders are capable of having profound effect on their followers. They inspire followers to go beyond their self-interest for the benefit of the organisation. (Robbins, 1984) They create a vision of a desired future and create commitment to achieve that goal. Leaders are require to have a deep understanding of organisations to achieve transformation change and to be able to convince followers to face the challenge. (Morgan, 1989) Transformation leaders are often being charismatic and passionate about leading, changing and improving their organisations. Therefore, followers are more likely to be motivated by leaders who have such characteristics, for example, Richard Branson and Bill Gates from the organisational world have attracted significant media and academic interest. (Brooks, 2009)
Poor leadership on subordinates will lead to business failure. Let’s look at Blackberry case, Blackberry has been the most successful smartphone maker in the world. Unfortunately, they were losing after being unable to adapt the growth of iPhone and Samsung. (Finkelstein, 2013) Poor leadership is one of main factor behind the company failure which relates to nepotism. This company promotes people from within based on tenure instead of people with skills and high potentials. Innovation is important in this industry, therefore, skills and potential people must not be side-lined. This company failed to see the importance of balancing both tenure and skilful people to maintain the growth of the company. A company will surely sink if the primary reason for a promotion is not focusing on competency. (Mick, 2013)
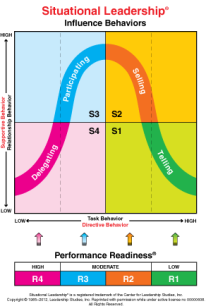
The situational approach to leadership developed by Dr. Paul Hersey in the late 1960s is a powerful model which refers to a leader or manager must adjust his style to fit the development level of the followers he is intend to influence. It is a flexible tool that enables leaders to influence others more effectively as leaders may change their style continually to meet the needs of others in the organisation based on the situation. This model highlights on 4 leadership styles – Delegating style, Participating style, Selling Style and Telling style. (Anthony, 2015)
However, although situational theories focus very much on encouraging leaders to adapt their leadership style based on difficult situation but there are little attention is paid to organisational culture or organisational politics. Therefore, this approach may not be the best leadership approach even though it serves several good methods to manage a team. This approach neglects interpersonal relationships within an organisation and it can have a negative influence or impact on performance in an organisation. (Brooks, 2009)
In conclusion, I personally believe that empowerment is very imporant. Credits given necessary is good as well as to give confidence to subordinates which is known as reward power. However, a manager should be more flexible to avoid creating tension within an organisation. Tension often leads to conflict, frustration and dissatisfaction. Besides that, a manager must be able to keep a good relationship with he or her subordinates by constantly engaging with them with regards to the work and also problem solving. I strongly believe that a good working environment will empower subordinates to perform better at work.
References
1. Anthony, L. (2015) ‘Defined Situational Leadership’ [online] available from http://smallbusiness.chron.com/define-situational-leadership-2976.html [accessed 5th March 2015]
2. Brooks, I. (2009) Organisational Behaviour: Individuals, Groups and Organisation, 4th edn. Pearson Education Limited.
3. Fayol, H. (1949) General and Industrial Management. London: Pitman Publishing.
4. Finkelstein, S. (2013) ‘The worst CEOs of 2013‘, BBC [online] available from http://www.bbc.com/capital/story/20131212-the-worst-ceos-of-2013 [accessed 5th March 2015]
5. Handy, C. (1993) Understanding Organizations. London: Penguin.
6. Kotter, J. (1990) A Force for Change: How Leadership differs from Management. New Tork: Free Press.
7. Mintzberg, H. (1973) The Nature of Managerial Work. New York: Harper & Row.
8. Mick (2013) ‘5 Businesses Sunk by Poor Leadership‘ [online] available from http://www.leader-values.com/wordpress/5-businesses-sunk-by-poor-leadership-anna-johansson/ [accessed 5th March 2015]
9. Morgan, G. (1989) Creative Organization Theory. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
10. Robbins, S. P. (1984) Essecntial of Organizational Behaviour, 3rd edn. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall
11. Zeleznik, A. (1977) ‘Managers and leaders: Are they different?’, Havard Business Review

Reblogged this on 7 Degrees Of Freedom.
LikeLike
In my opinion, i think to become an effective manager/leader, you should have both management and leading skills in order to reach organisation’s goal. What’s do you think ?
LikeLike
Nice blog. The fine difference between leadership and management is well defined.
LikeLike
I do really agree that transformational leadership is the most important style that a leader must have, however, I do not agree that it is the most effective leadership style because as you said above, it depends on the circumstances. Even, situational leadership could be better than transformational leadership in some circumstances. Do not you think so?
LikeLike